Describe How Cells Use Energy to Do Work
Recently Earl attended a picnic at his daughters school. Contributions included hamburgers hot dogs baked beans potato chips potato salad coleslaw apple pie and vanilla ice cream.
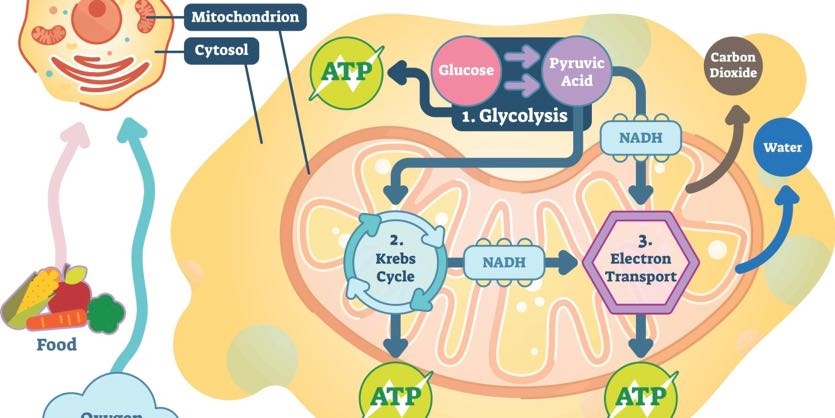
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists
As you can see from Figure 59.

. Cells release energy from ATP molecules by subtracting a phosphate group. The picnic was a potluck and the food was served outdoors. Now its back to being ADP and is ready to store the energy from respiration by bonding with a 3rd phosphate group.
The second ionization energy is energy to remove a second electron and is greater than that required to remove the first electron. While every location on Earth receives some sunlight over a year the amount of solar radiation that reaches any one spot on the Earths surface varies. Energy provided by ATP is used in active transport to contract muscles to make proteins and in many other ways.
Cellular processes such as the building and breaking down of complex molecules occur through step-wise chemical reactions. This energy is derived from the chemical bond energyin food molecules which thereby serve as fuel for cells. Cells require energy to perform work.
The photons from the light particles hit the photovoltaic panels that are essentially creating a current from the dislodged electrons from the semiconductor material. At the anode site the hydrogen molecules are split into electrons and protons SOLAR CELLS Solar cells are photovoltaic cells usually used for powering homes. Cells contain only a small amount of ATP at any one time.
As we have just seen cells require a constant supply of energy to generate and maintain the biological order that keeps them alive. This electricity can then be used to power a load such as a light or a tool. The living cells of every organism constantly use energy to survive and grow.
However glucose the simplest of them all is the only form that can enter the cell and actually gets used. A fuel cell consists of two electrodesa negative electrode or anode and a positive electrode or cathodesandwiched around an electrolyte. Synthesizing large molecules diffusion of substances down their concentration gradient moving chromosomes in cell division active transport of substances across the membrane synthesizing large molecules moving chromosomes in cell division.
A number of solar cells electrically connected to each other and mounted in a support structure or frame is called a photovoltaic module. One-Way Flow of Energy The sun is lifes primary energy source Producers trap energy from the sun and convert it into chemical bond energy All organisms use the energy stored in the bonds of organic compounds to do work There is a tendency for. The Solar panels collect the light and turn it into a current.
Solar radiation is light also known as electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by the sun. In a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell a catalyst separates hydrogen atoms into protons and electrons which take. So once muscle contraction starts the making of more ATP must start quickly.
Solar energy is used directly from the sun. The cell uses carbohydrates as its main source of energy. Other forms of carbohydrates including fructose lactose sucrose and starches must first be broken down into glucose before being absorbed.
ADP and ATP constantly convert back and forth in this manner. A fuel such as hydrogen is fed to the anode and air is fed to the cathode. Attaching a wire will harness the free electrons in the form of a charge.
Muscle cells may consumer energy to build long muscle proteins from small amino acid molecules. Cells break down complex carbohydrates into simple sugars that the cell can use for energy. During the light reactions of photosynthesis energy is provided by a molecule called adenosine triphosphate ATP which is the primary energy currency of all cells.
The first ionization energy of an atom is the energy needed to remove one electron completely. Some of these chemical reactions are spontaneous and release energy whereas others require energy to proceed. Solar technologies capture this radiation and turn it into useful forms of energy.
Cells release energy from molecules such as glucose in a process very similar to inhalation of air and exhalation of carbon dioxide by humans a process known as cellular respiration When a molecule loses hydrogen atoms as opposed to hydrogen ions it becomes. The second stage of cellular respiration the Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix. However ATP is not stored to a great extent in cells.
6 a mitochondrion has an inner and outer membrane. Energy is obtained from extracellular sources. Energy Select all of the cellular processes that require ATP.
Within 24 hours of the picnic. When the cell needs energy to do work ATP loses its 3rd phosphate group releasing energy stored in the bond that the cell can use to do work. They regenerate it from ADP as they need it using energy stored in food.
The space between the inner and outer membrane is called the intermembrane space. Applying The Scientific Method to Everyday Life. Modules are designed to supply electricity at a certain voltage such as a common 12 volts system.
The source of energy that is used to power the movement of contraction in working muscles is adenosine triphosphate ATP the bodys biochemical way to store and transport energy. A fuel cell works by passing hydrogen through the anode of a fuel cell and oxygen through the cathode. Ionization energy is the form of energy that binds electrons to the nucleus of its atom ion or molecule.
The process of photosynthesis by producers such as algae and green plants can convert light energy into chemical. Just as the dollar is used as currency to buy goods cells use molecules of ATP as energy currency to. The space enclosed by the inner membrane is called the matrix.
Scientists use the term bioenergetics to describe the concept of energy flow through living systems such as cells.

Specialized Cell Poster Science Poster Biology Classroom Science Lesson Plans

Biology Flow Chart For Cellular Respiration Complete Respiration Flow Chart Cellular Respiration Fr Teaching Biology Biology Classroom Medical Student Study

Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable

Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable

Cellular Aerobic Energy Production Also Known As Cellular Respiration Aerobic Oxidation And Oxidative Phosphorylation Cellular Respiration Oxidative Phosphorylation Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration

Energy And Metabolism Boundless Biology

Nutrient Metabolism Human Learn Science At Scitable

Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable
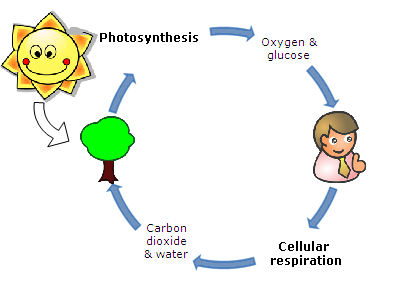
What Is The Purpose Of Cellular Respiration Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
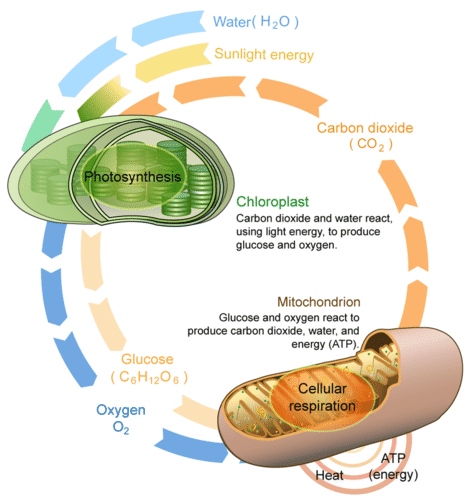
Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica

What Is Solar Energy Worksheet Education Com What Is Solar Energy Solar Energy For Kids Solar Energy Projects

Http Www Electronicsandyou Com Solar Energy Journal Uses Types Benefits Html Photovoltaic Cells Pv Cells How Solar Energy Works

Metabolism How Do Your Cells Release Energy From Food Free High School Curriculum High School Curriculum Science Education School Of Medicine

Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable

Cell Processes Energy Nitty Gritty Science Cell Processes Photosynthesis Activities Interactive Science Notebook
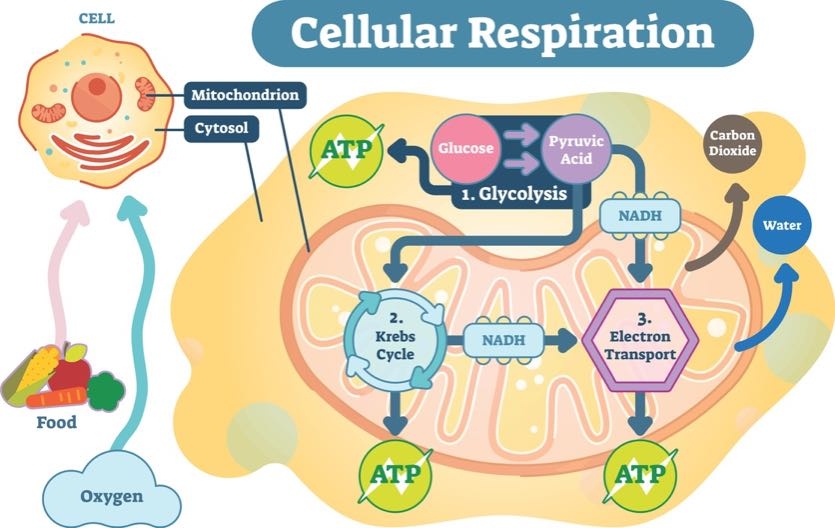
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists

Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable

How Solar Cells Work Green Education Sustainability Education Middle School Lessons
Comments
Post a Comment